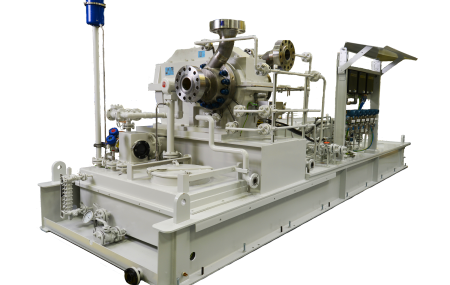
OIL AND GAS:
API 610 Centrifugal Pumps for General Refinery Service
This International Standard specifies requirements for single and multistage centrifugal pumps, including pumps running in reverse as hydraulic power recovery turbines, for use in petroleum, petrochemical and gas industry process services. This Standard is applicable to overhung pumps, between-bearings pumps and vertically-suspended pumps. This Standard is not applicable to seal-less pumps.
API 685 Seal Less Centrifugal Pumps
This standard covers the minimum requirements for seal-less centrifugal pumps for use in petroleum, heavy duty chemical and gas industry services. Single stage pumps of two classifications, magnetic drive pumps (MOP) and canned motor pumps (CMP), are covered by this standard.
API 674 Positive Displacement Pumps. Reciprocating
This standard covers the minimum requirements for reciprocating positive displacement pumps for use in service in the petroleum, chemical, and gas industries. Both direct-acting and power-frame types are included.
API 675 Positive Displacement Pumps. Controlled Volume
This standard covers the minimum requirements for controlled volume positive displacement pumps for use in service in the petroleum, chemical, and gas industries. Both packed-plunger and diaphragm types are included. Diaphragm pumps that use direct mechanical actuation are excluded.
API 676 Positive Displacement Pumps. Rotary
This standard covers the minimum requirements for rotary positive displacement process pumps and pump units for use in the petroleum, petrochemical, and gas industry services.
ISO 13709 Centrifugal Pumps for Petroleum, Petrochemical and Natural Gas Industries
This International Standard specifies requirements for centrifugal pumps, including pumps running in reverse as hydraulic power recovery turbines, for use in petroleum, petrochemical and gas industry process services. This International Standard is applicable to overhung pumps, between-bearings pumps and vertically suspended pumps. It is not applicable to seal/less pumps.
PROCESS:
ISO 9905:1994 Technical specifications for centrifugal pumps. Class I
The technical requirements refer only to the pump unit. Includes design features concerned with installation, maintenance and safety of such pumps, including baseplate, coupling and auxiliary piping. The selection of the class to be used is made in accordance with the technical requirements for the application for which the pump is intended. The class chosen is to be agreed between purchaser and manufacturer/supplier.
ISO 5199:2002 Technical Specifications for Centrifugal Pumps. Class II
This International Standard specifies the requirements for Class II centrifugal pumps of single-stage, multistage, horizontal or vertical construction, with any drive and any installation for general application. Pumps used in the chemical process industries (e.g. those conforming to ISO 2858) are typical of those covered by this International Standard. This International Standard includes design features concerned with installation, maintenance and safety for these pumps including baseplate, couplings and auxiliary piping, but it does not specify any requirements for the driver other than those related to its rated power output.
ISO 9908:1993 Technical specifications for centrifugal pumps. Class III
Covers class III requirements for centrifugal pumps of single stage, multistage, horizontal or vertical construction (coupled or close-coupled) with any drive and any installation for general application. Includes design features concerned with installation, maintenance and safety of such pumps including baseplate, coupling and auxiliary piping but excluding the driver, if it is not an integral part of the pump.
ISO 14847:1999 Rotary positive displacement pumps. Technical requirements
This standard specifies the technical requirements, other than safety and testing, for rotary positive displacement pumps and rotary positive displacement pump units. This standard does not apply to rotary positive displacement pumps for fluid power applications.
ISO 15783:2002 Seal. Less centrifugal pumps. Class II · Specification
This International Standard specifies the requirements for seal-less centrifugal pumps that are driven with permanent magnet coupling (magnet drive pumps) or with canned motor, and which are mainly used in chemical processes, water treatment and petrochemical industries. Pumps will normally conform to recognized standard specifications (e.g. ISO 5199, explosion protection, electromagnetic compatibility), except where special requirements are specified herein. This International Standard includes design features concerned with installation, maintenance and operational safety of the pumps, and defines those items to be agreed upon between the purchaser and manufacturer/supplier.
ISO 16330:2003 Reciprocating positive displacement pumps and pump units’ Technical requirements
This International Standard specifies the technical requirements, other than safety and testing, for reciprocating positive displacement pumps and pump units. It applies to pumps which utilize reciprocating motion derived from crankshafts and camshafts and also direct-acting fluid driven pumps. It does not apply to reciprocating positive displacement pumps, nor pumping water, where the whole pump is lubricated with the liquid being pumped.
ANSI/ASME 873.1 Specification for Horizontal End Suction Centrifugal Pumps for Chemical Process
This standard covers centrifugal pumps of horizontal, end suction single stage, center-line discharge design. This Standard includes dimensional interchangeability requirements and certain design features to facilitate installation and maintenance. It is the intent of this Standard that pumps of the same standard dimension designation from all sources of supply shall be interchangeable with respect to mounting dimensions, size and location of suction and discharge nozzles, input shafts, baseplates, and foundation bolt holes.
ANSI/ASME 873.2 Specifications for Vertical Inline Centrifugal Pumps for Chemical Process
This Standard covers motor-driven centrifugal pumps of vertical shaft, single stage design with suction and discharge nozzles in line. It includes dimensional interchangeability requirements and certain design features to facilitate installation and maintenance. It is the intent of this Standard that pumps of the same standard dimension designation, from all sources of supply, shall be interchangeable with respect to mounting dimensions and size and location of suction and discharge.
ASME 873.3 Specification for Seal.less Horizontal End Suction Metallic Centrifugal Pumps for Chemical Process
This Standard covers seal-less centrifugal pumps of horizontal end suction single stage and centre-line discharge design. This Standard includes dimensional interchangeability requirements and certain design features to facilitate installation and maintenance. It is the intent of this Standard that pumps of the same standard dimensional designation from all sources of supply shall be interchangeable with respect to mounting dimensions, size, and location of suction and discharge nozzles, input shafts, baseplates, and foundation bolt holes
ASME 873.5M Specification for Thermoplastic and Thermoset Polymer Material Horizontal End Suction Centrifugal Pumps for Chemical Process (not often used in Australia)
This Standard covers centrifugal pumps of horizontal, end suction single stage, centreline discharge design, which components are made of thermoplastic and thermoset polymer materials either reinforced or non-reinforced. It includes dimensional interchangeability requirements and certain design features to facilitate installation and maintenance. It is the intent of this Standard that pumps of the same standard dimension designation from all sources of supply shall be interchangeable with respect to mounting dimensions, size, and location of suction and discharge nozzles, input shafts, baseplates, and foundation bolt holes. This Standard does not include lined or non polymer components.
ANSI/HI 3.1.3.5 Rotary Pumps (not often used in Australia)
This standard applies to industrial rotary positive displacement pumps. It includes: types and nomenclature; definitions; design and application, operation and maintenance. The updated standard also includes:
• Capability tables in both metric and US customary units providing comparisons of rate of flow, pressure, viscosity, solids and abrasive handling, reversible rotation, and power range for 11 different types of rotary pumps;
• A consolidated range chart providing a comparison of pressure and rate of flow in both metric and US customary units for 11 different rotary pump types;
• Detailed explanation of each rotary pump type including basic operation, design features, typical applications, and driver requirements;
• New and updated cross-sectional illustrations of popular rotary pump designs;
• Revised and expanded list of definitions;
• Listing of viscosities of common fluids;
• Plot of efficiency vs. rate of flow for different pump types;
• A completely new section on multiphase pumps for oil and gas applications.
ANSI/HI 4.1.4.6 Seal.less Rotary (not often used in Australia)
This standard applies to industrial rotary positive displacement pumps. It includes: types and nomenclature, definitions; design and application; installation, operation and maintenance; and test. It does not include standards on magnetic drives for seal-less pumps.
ANSI/HI 5.1.5.6 Seal.less Centrifugal Pump Standards (not often used in Australia)
This standard is for seal/less centrifugal pumps that are driven by canned motors or magnetic couplings. It includes types and nomenclature; definitions; design and application; installation, operation/maintenance and testing. The testing section includes:
• Hermetic Integrity Test
• Mechanical Integrity Test
• Winding Integrity Test
ANSI/HI 6.1.6.5 Reciprocating Power Pump Standard (not often used in Australia)
This Standard applies to industrial/commercial reciprocating power pumps. It includes:
• Types and Nomenclature
• Oefinitions
• Design and Application
• Basic Speeds
• Pump Torque Characteristics
• Calculating Volumetric Efficiency
• Installation
• Protection of Pump Against Seepage or Flood
• Orive Alignment after Piping Installation
• Operation and Maintenance
ANSI/HI 7.1.7.5 Controlled Volume Metering Pumps (not often used in Australia)
This Standard applies to Controlled-Volume Metering Pumps, which are reciprocating power pumps used to accurately displace a predetermined volume of liquid within a specified time. It contains sections on:
• General Oescription
• Types and Nomenclature
• Oefinitions
• Application and sizing
• Typical performance curves
• Materials of construction
• Control methods
• Installation
• Storage recommendations
• Operation and trouble solving
ANSI/HI 10.1.10.5 Air Operated Pumps (to our knowledge the only standard available for this type of pump and to date not seen in Australia)
This standard is for air-operated pumps and includes those positive displacement reciprocating pumps used for general fluid transfer, which are driven by means of a compressed gas (usually air) from an outside source. The pump may be designed with a single diaphragm or double diaphragms connected to a reciprocating shaft in which one side of the diaphragm is in contact with the liquid being pumped and the other side is in contact with the compressed gas. The standard includes the following sections:
• Types, configurations, and nomenclature
• Oefinitions
• Oesign and Application
• Installation, Operation, and Maintenance
ANSI/HI 12.1.12.6 Centrifugal Slurry Pumps (not often used in Australia)
This standard for centrifugal slurry pumps for nomenclature, definitions, applications and operation addresses a long-standing challenge in the wastewater pump industry for development and acceptance of a test standard written specifically for slurry pumps. The scope of this standard includes:
• Slurry pump types
• Types of slurries
• Slurry limitations
• Slurry solids effect on pumps
• Pumping of froth, pump wear, and application
The standard provides requirements for wet-end and bearing housing shaft seals, establishes allowable nozzle loads, and provides a data sheet that can be used by purchasers and vendors to exchange information.
GENERAL PURPOSE:
ISO 2858:1975 End.suction centrifugal pumps (rating 16 bar) .. Designation, Nominal duty point and Dimensions
The standard covers the ISO requirements for general purpose pumps primarily for use with water. The pump designation consists of three numbers detailing suction and discharge connection sizes and nominal impeller diameter in mm e.g. 125 x 100-250. The table covers flange sizes from 50 mm up to and including 200 mm. This is primarily a dimensional standard.
DIN 24255 End.suction centrifugal pumps (normal rating 10 bar although some may claim 16 bar)
This specification details single stage, end suction overhung impeller centrifugal pumps for general purpose applications design to be used primarily with water up to a maximum of 120 C. This is primarily a dimensional standard. The majority of OIN 24255 pumps supplied in Australia are manufactured in China.